Birefringent components are a special type of optical components that exhibit birefringence.
That is, the refracted light propagates in two directions: ordinary light (o light) and extraordinary light (e light ). Phase retardation refers to the phase difference between o light and e light when light passes through a birefringent component. The size of the phase retardation is related to factors such as the material properties, geometry of the component, and the wavelength of the incident light. Accurately measuring the phase retardation of birefringent components is of great significance for the design and performance evaluation of optical systems.
For example, in optical fiber communication systems, the measurement of phase retardation can be used to measure the dispersion characteristics of optical fiber, thereby optimizing the bandwidth and transmission distance of optical fiber transmission. In imaging equipment such as optical microscopes and optical coherence tomographs, the measurement of phase delay can be used To improve resolution and accurately measure the surface topography of samples.
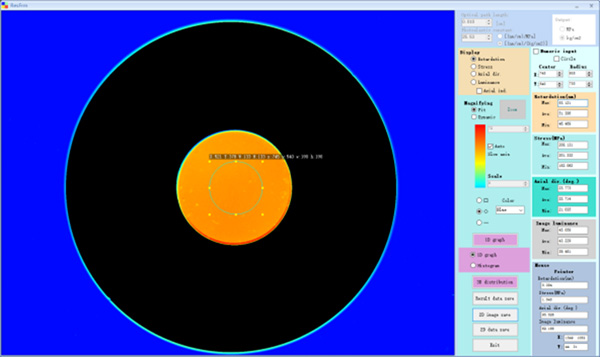
The specific method for high-precision detection of phase retardation within birefringent components adopts the principle of photoelasticity.When light travels through a polarizer, it becomes circular polarized light. When a phase-delayed sample is placed, there is an optical retardation between the slow axis and fast axis . Thus the outgoing light becomes elliptical polarized light. By rotating the analyzer, the rotating angle of the polarized light which is affected by the presence of phase retardation can be detected precisely.Below automatic Polariscope is an measuring instrument to precisely measure phase retardation.